Importance of Secure SDLC
In Today's world, security has become necessary, and software security is one of the most critical aspects. Many web applications exist in the market to make our lives easier and much more enjoyable. We can pay bills online, chat with friends, shop online or communicate with people worldwide. For many of us, web applications have brought convenience, but these applications' perceptions may differ from person to person.
"Software security is about making software behave correctly in the presence of a malicious attack."
It protects information and systems from unauthorized access, disclosure, use, disruption, and destruction. These can be represented through the CIA Triad, as shown below:
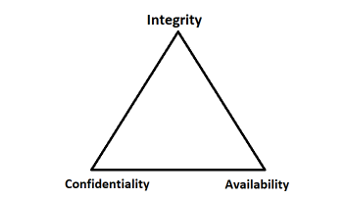
To develop secure applications, Security checks should be made throughout the application project lifecycle, especially when the application deals with critical information and data.
Security Development Life Cycle (SDL) Framework:
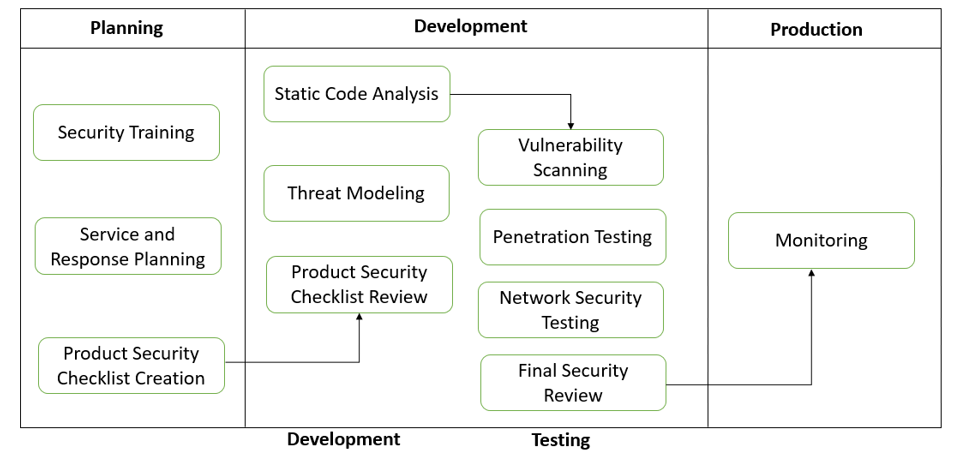
A Secure Development Life Cycle has 3 main phases, i.e., Planning, Development, and Production, which again consists of other sub-phases.
Planning:
- Security Training: This is one of the prerequisites. Some basic concepts for building good quality software include secure design, threat modeling, secure coding, security testing, and best practices surrounding privacy.
- Service and Response Planning: Preparing a security project production service plan and an incident response plan.
- Product Security Requirement Checklist: Prepare security checkpoints as per business requirements; they are majorly divided into 2 categories internal needs and business requirements(B&FS Domain, E-Commerce, etc.)
Development:
- Product Security Checklist Review: The security team reviews the identified checklist and development team and does prioritizations based on feasibility and business needs. In this phase security the development team also identifies standard and reusable components.
- Threat Modeling: Potential threats can be identified and organized/prioritized through the Threat modeling process. Threat modeling provides a systematic analysis of the potential attacker's profile, the most likely attack vectors, the assets most desired by an attacker, and a catalog of potential threats that may arise.
- Static Code Analysis: Static program analysis is performed without practically executing the programs. It is also called Source Code Analysis. It is an attempt to highlight possible vulnerabilities within 'static' (non-running) source code. Tool– OWASP LAPSE+
- Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning is an automated approach to finding security vulnerabilities in software. These tests can be run as part of vulnerability management by attackers looking to gain unauthorized access.
- Final Security Review: The Final Security Review (FSR) examines all security activities performed on software before the release. This activity includes examining threat models, tool outputs, and performance against the quality gates and bug bars defined during the requirements phase.
Production:
- Monitoring and Process Improvement Plan (Training): Once a problem is identified in a production environment; the security team makes sure that the same problem should be addressed in the planning and design phase only. They train resources according to that.
SDL Guidelines in ICT (Information and Communications Technology Industry):
- Authentication and Password Management:
- Validate the user with his identity and make sure that he is what he claims to be. Authentication is commonly performed by submitting a username/ID and one or more items of private information that only the user would know.
- Password management system should be designed to store, organize, and encrypt passwords for online accounts on several devices. It is a better and safer alternative to reusing the same two or three passwords.
- Session Management:
- Session management should be implemented as an exchange mechanism that will be used between the user and the web application to share and continuously exchange the session ID.
- Checking URLs in the restricted areas, checking exposed Session variables, testing the cookie attribute using intercept proxies, etc., are few checkpoints in Session Management testing.
- Access Control: It should be implemented to ensure that an authenticated user accesses only what they are authorized to and no more.
Vulnerability Scanning Example:
Here is an example of vulnerability scanning. A vulnerability scanner sends special data to your web application – the type of data that a malicious hacker would send, but it does it safely.
- Vulnerability View: After scanning the web application Checkmarx tool reports 4 "SQL Injection" vulnerabilities.
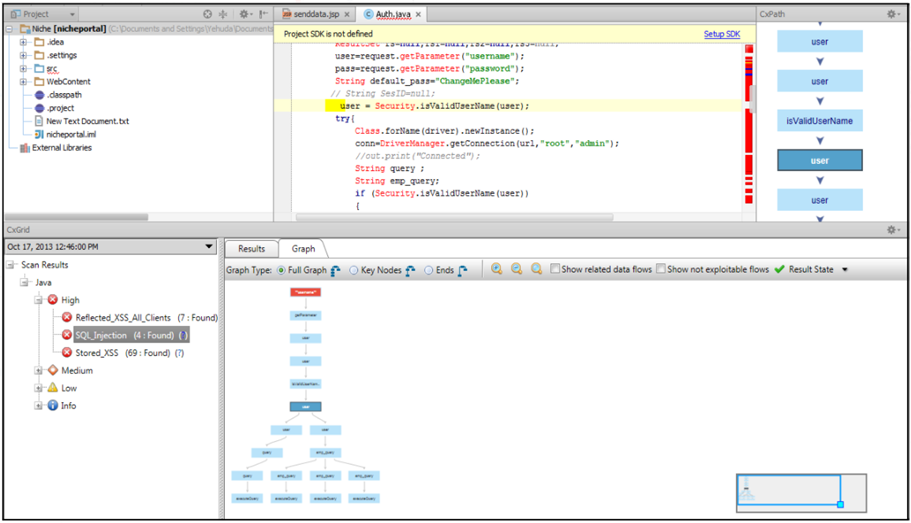
- 2. Result View: This view will show the source code folder, file name, line number, and other details related to other vulnerabilities, which will help development teams to apply fixes at specific locations.
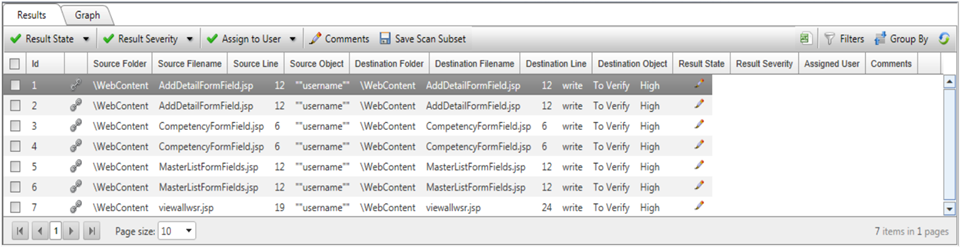
- Once development teams apply fixes, they rerun scans and check that vulnerabilities are appropriately fixed or not.
To Conclude, see if your organization already follows Secure SDLC. If not, start now. And if it already does, know that there's always room for improvement! Threats and attacks are evolving every day, and if you are not cautious enough, they may jeopardize your company's reputation and credibility. The best way to keep your software safe from this menace is to implement security measures throughout the development process.
Relevant blog: Oracle EBS Apps Security
Comments
Post a Comment