They’re Here: Enterprise Mobile Apps Have Arrived
While the consumer mobile app
market continues to grow by leaps and bounds, enterprise mobile apps lag behind
their consumer counterparts. VisionMobile projects that these markets will
double in size in the next few years, reaching $58 billion by 2016–and that’s
just in North America. Read more about Custom
application development.
Trend – Mobile devices are more powerful than ever
Trend – There’s a mobile app dev option for everyone
 These three major development options let
mobile app producers create products in a variety of methods. Depending on your
situation, there’s a method for you.
These three major development options let
mobile app producers create products in a variety of methods. Depending on your
situation, there’s a method for you.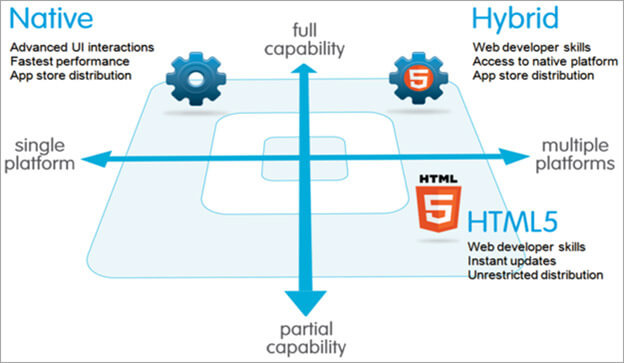
Trend – Incorporate security into your mobile app development

Trend – Start using new development processes

Native App Dev Process
Mobile Web App Dev Process
Hybrid App Dev Process
Trend – Tablets are becoming the business device of choice
Trend – Generating income with enterprise business apps

The free business app model
The white label app store model
Trend – Explore vertical marketplaces
Expanding your existing customer base
The mobile landscape is changing rapidly
These numbers however, refer mainly to the
non-business world. Apps are pretty ubiquitous in our personal lives, as we
play games, check our bank balances, and control our home alarm systems through
apps on our smartphones and tablets. In the business world, however, adoption
rates are notoriously slow. It’s not surprising, since enterprise companies
have longer processes to spend their money. Or adopt new technologies.
Enterprises dipped their toes in the mobile
world through mobile devices like iPhones and tablets for executives. As
they’ve become more comfortable with the notion of efficiency, optimization,
and productivity for their employees, they’ve expanded their enterprise mobile
apps view. Apps to handle CRM, accounting, and IT started popping up in the
enterprise environment. The number of mobile apps that they’re looking at and
purchasing is increasing every year, as their comfort level with the idea of
mobile increases.
Surprisingly, it’s not just the
traditionally forward-thinking industries that are going mobile–industries like
healthcare, banking, government, and insurance are just a few that are becoming
increasingly mobile. They’re all improving their infrastructure and developer
processes to align themselves to the next phase of mobile innovation. They’re
getting ready, are you?
Whether you’re already producing mobile apps
for the enterprise market, or are considering jumping into it now, we’ve
noticed a number of trends in the enterprise app development world that we’d
like to share.
Trend – Mobile devices are more powerful than ever
Mobile device chip producers are creating
processors that are better able to handle the high-power tasks we do on them,
like streaming video, working in the cloud and essentially acting like
mini-computers for us. For example:
·
Qualcom’s
Snapdragon 800 supports Ultra HD video resolution, cameras up to 55 megapixels,
and has a top processing speed of 2.3 GHz.
·
Samsung’s
Exynos 5 Octa has two cores (a 1.2 and a 1.8) that work in concert to decrease
overall power consumption without degrading your performance experience.
·
Apple’s
A7 is the world’s first 64-bit processor for mobile use and has twice the
graphics speed as it’s A6 predecessor.
This means that your apps can use more of the
mobile device than ever. For example, accessing the camera, microphone, GPS, or
gyroscope, and displaying rich UIs and graphics. Your app can also run offline
and on multiple mobile platforms (iOS, Android, or Windows) without much
difficulty.
Trend – There’s a mobile app dev option for everyone
 These three major development options let
mobile app producers create products in a variety of methods. Depending on your
situation, there’s a method for you.
These three major development options let
mobile app producers create products in a variety of methods. Depending on your
situation, there’s a method for you.
Native
applications are
apps developed for a specific mobile operating system with the O/S-specific
programming language and software development kit (SDK). For example, iOS apps
are developed in Xcode and objective C, while Android apps are developed with
Java. These apps are downloaded to the user’s mobile device and accessed
separately from other functions on the device.
Mobile
Web applications are
essentially Internet-enabled apps that are accessed via the mobile device’s web
browser. Developers create apps that use the powerful capabilities of the
device’s web browser to display the app, and users don’t have to download
anything.
Hybrid
applications are
apps that combine native development with web technology. Developers combine
web development methodologies and the native app APIs to create an app that’s
distributed through the native app stores.

Trend – Incorporate security into your mobile app development

According to new data from F-Secure, the majority
of all malware threats were created for Android mobile devices, but that’s not
to say that iOS or Windows were immune either. F-Secure found that 91% of these
threats were malware, with most of those being Trojans that silently sent SMS
messages to premium-rate numbers or subscription services. Others downloaded
and installed unsolicited files or apps onto the mobile device, while others
silently tracked the device’s GPS location without the user’s knowledge.
Security is one
of the main reasons that enterprises have been reticent to use mobile apps,
so ensuring that your mobile app is secure is key. Remember, enterprises guard
their business information through NDAs and other legal entities, so help them
guard their intellectual property with the right levels of security.
Trend – Start using new development processes

Along with the technical options you have
while producing your enterprise business mobile app, there also some
development process options you should incorporate.
·
Agile
software development processes can help you be collaborative and flexible, and
protects your app from adopting the “wrong” technology, and lets you pivot
quickly and efficiently.
·
Incorporate
security into your development lifecycle. Determine how to embed security into
all layers of your app, as you develop it, not after you’re done.
·
Use
automated testing methods and tools to root out all the bugs in your app.
Automated tools let you test across numerous variables, situations, mobile
devices, and platforms.
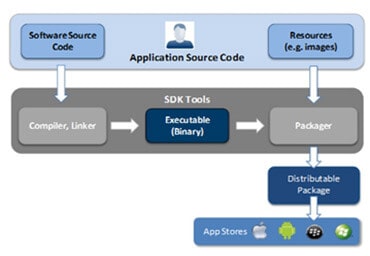
Native App Dev Process

The native app dev process
includes the obvious things like writing the source code, compiling it,
bundling it with the appropriate resource files, as well as the OS-specific
APIs that the app needs to function, like access to the device’s data storage,
GPS information, camera, etc. It also includes tasks like following the process
of the appropriate app store to have your app distributed. The approval process
for each store can be lengthy and time consuming, so be sure to add this to
your overall process.
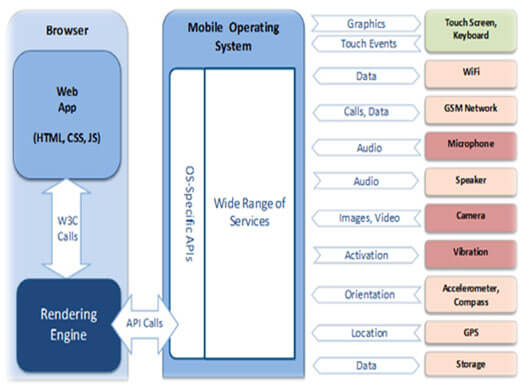
Mobile Web App Dev Process

Mobile web applications are run inside the
device’s web browser, and are developed with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Because
they run in the browser, as opposed to within the device’s OS framework, your
web app is a little easier to produce. Web apps are automatically
cross-platform compatible, however aren’t as robust as the native apps because
you don’t have access to the OS- specific APIs that give you access to the
device’s other functions.
Development can be handled by more generalist
staff, which gives you a potentially larger employment pool from which to draw.
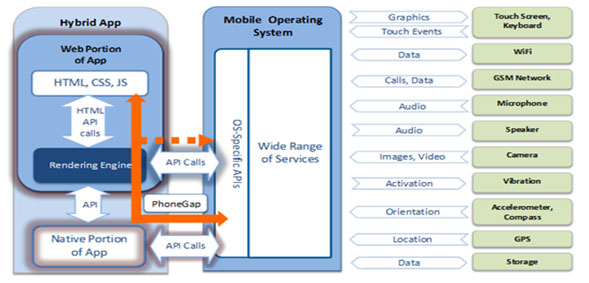
Hybrid App Dev Process

The hybrid app development environment is
really the best of both worlds–it gives you access to the best attributes of
the native and web app dev processes and products. You’re able to use the
cross-platform compatibility of the web app environment through HTML, CSS, and
JavaScript development, while also being able to access the device’s
OS-specific APIs and functions. That means your hybrid app can access the
device’s camera, data storage, and more.
To use this hybrid app dev process, you’ll
need the help of a bridge technology such as PhoneGap. PhoneGap lets you take
an existing code base and deploy to multiple mobile platforms, while giving you
access to the OS-specific APIs and therefore the device’s functions.
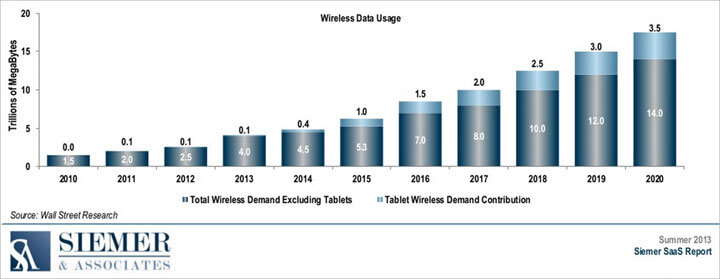
Trend – Tablets are becoming the business device of choice
According to the Siemer SaaS Report, the use
of tablets in enterprise planning will grow by nearly 50% annually. The amount
of bandwidth that tablets will use at the enterprise level will also grow
annually, accounting for nearly 20% of all mobile bandwidth use by 2020.
On a consumer tablet level, Android has
overtaken iOS, powering over 62% of the tablet market. At the enterprise
level however, Android has an anemic 8.4% of tablet activations. It’s tough
competing with the Apple juggernaut, however when you combine the fact that
users tend to consolidate their mobile phone and tablet devices to the same
operating system with a loosening of enterprise BYOD restrictions, you’ll see a
corresponding increase in the number of enterprise Android users. (Note: Current numbers
are a bit difficult to compare, as Apple numbers count only smartphones,
while Android ones include both smartphones and tablets.)

Producing mobile apps across all of these
platforms is going to be challenging for app producers, as you need to have
developers with the right kind of skills for those platforms. Here’s a quick
list of what you’ll need.

|

|

|

|
|
Languages
|
Objective C
|
Java
|
Java
|
.NET, C#
|
Tools
|
Xcode
|
Android SDK
|
BB Java Eclipse Plug-in
|
Visual Studio, Windows SDK
|
Executable Files
|
.ipa
|
.apk
|
.cod
|
.xap
|
App Store
|
Apple App Store
|
Google Play App Store, Amazon Appstore, GetJar
|
BlackBerry App World
|
Windows Phone Market
|
Trend – Generating income with enterprise business apps

Just like enterprise companies
need to shift their software purchasing policies, app developers need to
rethink the way they make money off their apps. Up to now, they’ve mainly done
it through in-app purchases, however they may be leaving a lot of money on the
table this way–well over $20 billion in the last two years,according to
VisionMobile. Custom apps generate 65% of app producer revenues right now, so
increasing their reach into better licensing deals and subscription services
are other ways to increase this.
The free business app model
Free consumer apps often generate income
through in-app purchases, so how can enterprise business apps generate it?
Simple, with a subscription service available outside the app store.
Enterprises can download the app for free, but to fully use it, they will need
a subscription to access all of the data the app can display and process. This
is an effective way to target prospects and convert them, as employee users are
the largest downloaders of apps, and are becoming freer to do so.
The white label app store model
Instead of releasing an enterprise business
app to Apple’s App Store or Google’s Play Store, tech suppliers are starting to
realize the value of having their own white label app store. Gartner estimates
that by the end of this year, 60% of IT organizations will have deployed
private app stores.
These customized app stores will let
enterprise businesses manage and deliver apps for computers, smartphones, and
tablets. Current providers include:
·
Apple’s
Volume Purchase Program for business
·
HP's recently
launched – HP Access Catalog
·
Apperian
Trend – Explore vertical marketplaces
We’re already seeing this in the healthcare
market, as mobile apps are being created for everything from medical reference
books to billing to tele-conference with doctors. These markets are looking to
improve their business processes and speed up efficiencies in their work
environments. Apps like drchrono,
and advisory committees like SMART (Substitutable
Medical Apps and Reusable Technology) are popping up to handle this need.
Expanding your existing customer base
Many companies won’t even need to go outside
of their company to expand their app customer base. Enterprise companies like
CDW and Accenture are becoming mobile app producers themselves. Just do a quick
search for “enterprise business app development” and you’ll see how many of the
big players are getting involved– everyone from CDW, to Accenture
(through their alliance with Crittercism), and Microsoft’s
Windows 8 Metro-Style apps are creating their own enterprise business
apps.
The main reason these companies are jumping
into the enterprise business app world is because enterprise purchasing
policies haven’t yet reached the Web 2.0 era, and so in order to expand their
customer base, they’re conforming to the existing policies. The smaller and
intermediate players are handling those companies that are more
forward-looking, however there’s still a need to handle the slower enterprise
behemoths.
The mobile landscape is changing rapidly
Changes are happening so rapidly, and in so
many areas of the mobile market that it’s hard to keep up. We’ve highlighted a
few of the trends we’re seeing, however we’d love to hear from you too. What
mobile app dev trends are you noticing in your market? Have you started working
on your own enterprise business app? How’s it going? Hit up the comments and
let us know. Learn more about Application Development
Solutions.
Original Source Blog: https://www.jadeglobal.com/blog/theyre-enterprise-mobile-apps-arrived
Comments
Post a Comment